BLOG & NEWS
- Business
- Cars
The future of EVs
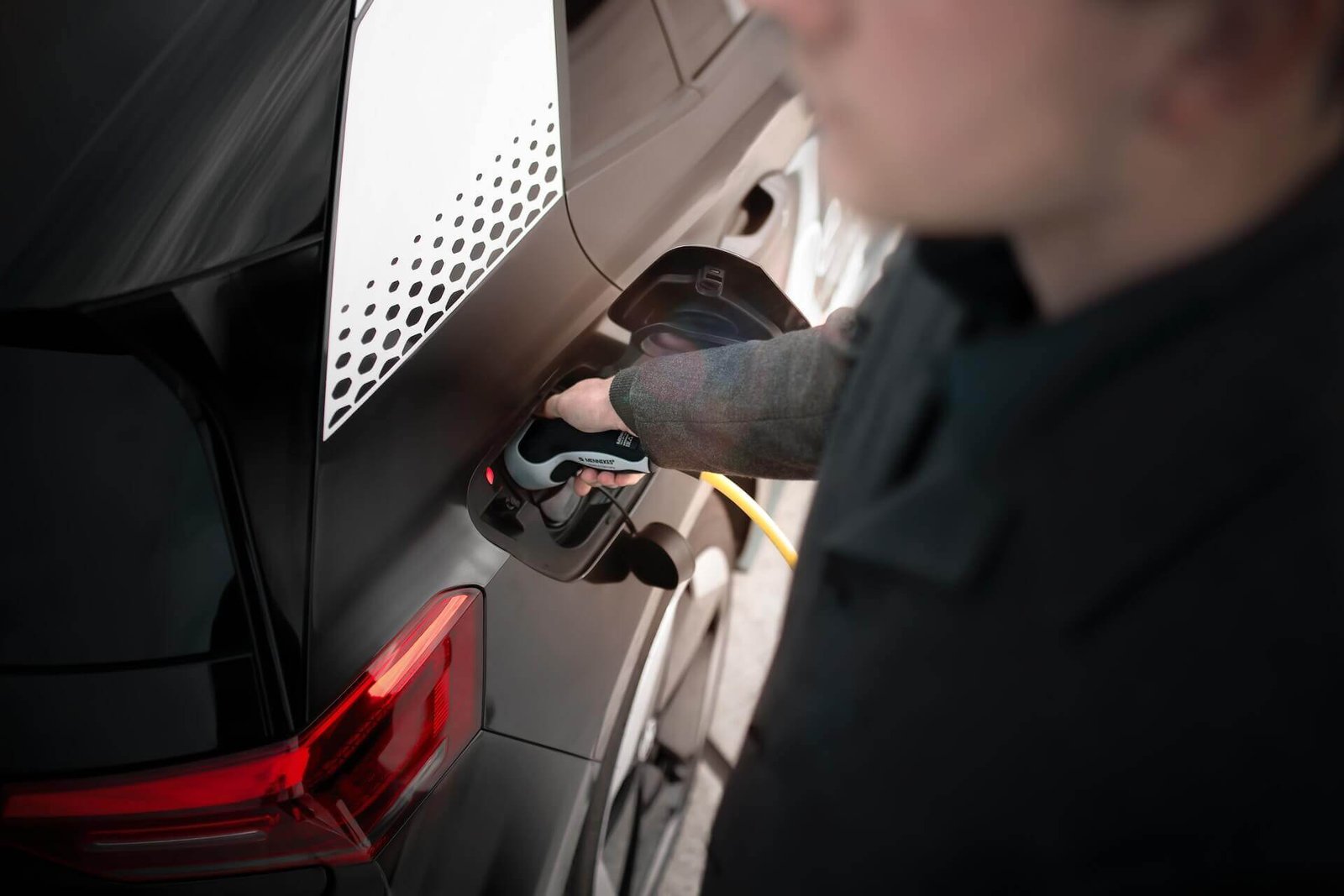

The future of EVs
October 9, 2023
The future of electric vehicles (EVs) looks bright, as more and more consumers are choosing to switch to electric power and governments and businesses are investing in the development of charging infrastructure.
One potential area of growth for EVs is in the development of autonomous vehicles, which are vehicles that are able to operate without the need for a human driver. Autonomous EVs have the potential to significantly improve safety and efficiency on the roads, and they are already starting to be tested in a variety of settings.
Another potential area of growth for EVs is in the development of new battery technologies. Current EV batteries have a limited range and can be expensive, which can be a barrier for some potential buyers. However, researchers are working on developing new battery technologies that are more energy-dense, longer-lasting, and more affordable, which could make EVs more appealing to a wider range of consumers.
Additionally, the growth of EVs is likely to be supported by an expansion of the charging infrastructure. As more and more EVs are sold, the demand for charging stations will increase, which will drive the development of new charging technologies and the expansion of the existing charging network.
Overall, the future of EVs looks bright, as new technologies and innovations continue to emerge and more consumers and businesses recognize the benefits of electric power.
- Blockchain
- Computing
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain Technology
September 2, 2023
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed ledger system that has gained widespread attention for its potential to revolutionize various industries. Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain stores data in a tamper-resistant, chronological chain of blocks. In this discussion, we will explore the fundamental concepts of blockchain, its applications beyond cryptocurrencies, and some of the challenges it faces.
At its core, a blockchain is a chain of blocks, each containing a batch of transactions. These blocks are linked together using cryptographic hashes, ensuring the integrity of the data. Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes virtually immutable, making it highly secure against tampering. Blockchains can be public, allowing anyone to participate, or private, with restricted access. Key features include decentralization, transparency, and consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
While blockchain's initial application was in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its potential extends far beyond digital money. It is increasingly used in various sectors such as supply chain management, where it enhances transparency and traceability. Blockchain also finds applications in identity verification, enabling individuals to have control over their personal information. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined rules, automate processes in fields like legal and finance. Moreover, blockchain can facilitate voting systems, reducing fraud and increasing trust in elections.
Despite its promise, blockchain faces several challenges. Scalability is a significant concern, as increasing the number of transactions can slow down networks and raise costs. Energy consumption, especially in PoW-based blockchains, has drawn criticism for its environmental impact. Regulatory and legal issues also pose challenges, as governments grapple with how to regulate this technology. Additionally, blockchain is still evolving, and standards for interoperability and security need further development.
Blockchain technology is still in its early stages, but its potential to disrupt industries is evident. As scalability and energy efficiency improve, and regulatory frameworks mature, blockchain adoption is likely to grow. Interoperable blockchain networks could enable seamless data sharing, and advancements in consensus mechanisms could enhance efficiency and security. In the future, blockchain may become an integral part of various sectors, transforming how data is stored, shared, and verified.
In conclusion, blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful innovation with the potential to reshape industries beyond cryptocurrencies. Its fundamental principles of decentralization and transparency offer solutions to long-standing challenges in data management and trust. While challenges persist, ongoing research and development efforts are paving the way for blockchain's integration into diverse applications, making it a technology to watch in the coming years.
- Computing
Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing
September 2, 2023
Quantum Computing is a cutting-edge field that explores the use of quantum-mechanical phenomena to perform computations. Unlike classical computers that use bits as the fundamental unit of information, quantum computers use quantum bits or qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to the principles of superposition and entanglement. In this discussion, we will explore the fundamentals of quantum computing, its potential applications, and some of the challenges it faces.
Quantum Computing Fundamentals:
Quantum computers leverage the unique properties of qubits to perform calculations at a scale that classical computers cannot achieve. Superposition allows qubits to represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously, and entanglement enables the state of one qubit to be dependent on the state of another, even if they are physically separated. Quantum gates manipulate these qubits to perform operations, and quantum algorithms harness these properties for solving specific problems more efficiently.
Potential Applications:
Quantum computing holds immense promise in various domains, including cryptography, optimization, drug discovery, and materials science. One notable application is in breaking current encryption methods, which could have both positive and negative implications for cybersecurity. Quantum computers can also revolutionize supply chain optimization, simulate quantum systems accurately, and discover new materials with extraordinary properties. These applications have the potential to reshape industries and scientific research.
Challenges in Quantum Computing:
Despite its potential, quantum computing faces several significant challenges. One key challenge is maintaining the stability of qubits. Qubits are highly susceptible to environmental factors like temperature and electromagnetic radiation, making error correction a daunting task. Developing error-correcting codes and stable qubit technologies is crucial for practical quantum computing. Moreover, building scalable quantum hardware remains a considerable engineering challenge, with quantum computers today being in their infancy.
Quantum Computing and the Future:
The growth of quantum computing is inevitable, and its impact on various industries will be profound. Organizations and researchers are racing to develop quantum hardware, algorithms, and applications. Quantum supremacy, the point at which quantum computers surpass classical computers in specific tasks, is an exciting milestone on this journey. As quantum technologies mature, we can anticipate transformative breakthroughs in cryptography, optimization, and scientific discovery, ushering in a new era of computing and problem-solving.
In conclusion, quantum computing represents a revolutionary shift in the world of computation. Its unique properties and potential applications make it a highly promising field, although it is still in the early stages of development. Overcoming the challenges associated with quantum computing will be essential for realizing its full potential and reshaping various industries in the years to come.
- DevOps
- Web
DevOps and CI/CD

DevOps and CI/CD
September 2, 2023
DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are two closely related practices that have revolutionized software development and deployment processes in recent years. They represent a paradigm shift in how software is built, tested, and delivered, enabling organizations to achieve faster release cycles, higher quality software, and improved collaboration between development and operations teams. In this discussion, we will delve into the core principles and benefits of DevOps and CI/CD, their role in modern software development, and some best practices for implementing them effectively.
DevOps is a cultural and technical approach that emphasizes collaboration, communication, and integration between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) teams. It aims to automate and streamline the entire software development lifecycle, from code development to production deployment. DevOps encourages a shared responsibility for the entire process, breaking down silos that often exist between these traditionally separate teams. Key principles include automation, continuous monitoring, and a focus on delivering value to the end-users.
Continuous Integration (CI) is a crucial component of DevOps. It involves the practice of frequently integrating code changes into a shared repository, where automated tests are run to ensure that new code does not introduce defects or break existing functionality. CI helps catch and fix issues early in the development process, reducing the likelihood of integration problems later on. It promotes a culture of frequent, small code changes and collaboration among developers.
Continuous Deployment (CD) takes CI a step further by automating the deployment process to production or staging environments after successful integration and testing. This means that every code change that passes CI tests is automatically deployed, reducing manual intervention and minimizing the time between writing code and delivering it to users. CD allows organizations to release new features and bug fixes rapidly, improving user satisfaction and competitive advantage.
The adoption of DevOps and CI/CD offers numerous benefits to organizations. These include faster time-to-market, increased software quality and reliability, reduced manual errors, improved collaboration among teams, and the ability to respond quickly to changing market demands. Additionally, DevOps and CI/CD provide greater visibility into the development and deployment process, enabling better tracking and management of software projects.
DevOps and CI/CD are transformative practices that have become essential in the software development landscape. They enable organizations to build, test, and deploy software more efficiently, with higher quality and faster release cycles. By fostering collaboration between development and operations teams and automating key processes, DevOps and CI/CD help organizations stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital world. Embracing these practices is not only a technological choice but also a cultural shift that can drive innovation and business success.
- Interfaces
- Web
The UI / UX in car infotainment systems
The UI / UX in car infotainment systems
March 3, 2023
The user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) in car infotainment systems are essential for providing a seamless and enjoyable experience for drivers and passengers. Here are some key considerations for designing a great UI/UX in car infotainment:
- Keep it simple: The interface should be simple and easy to navigate, with intuitive icons and minimal text. Avoid overwhelming the user with too many options.
- Prioritize safety: Safety should always be the top priority. The interface should be designed to minimize distractions while driving. For example, buttons and controls should be easy to reach and operate without taking the driver's attention away from the road.
- Consistency: Consistency in the UI design across different screens and functions is key to a good user experience. Users should be able to quickly understand how to navigate and operate the system.
- Visual appeal: The interface should be visually appealing, with high-quality graphics, colors, and animations that are easy on the eyes. This can enhance the user experience and make the infotainment system more enjoyable to use.
- Personalization: Users should be able to personalize the system to their liking. This can include setting preferences for things like music, climate control, and navigation.
- Feedback: The system should provide clear and timely feedback to the user when actions are taken. For example, buttons should visually respond when pressed, and audio feedback can be used to confirm actions taken by the user.
- Accessibility: The interface should be accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This can include features like text-to-speech, larger font sizes, and audio feedback for controls.
By focusing on these key considerations, designers can create an intuitive and enjoyable UI/UX for car infotainment systems that enhance the driving experience and keep users engaged and safe on the road.



